
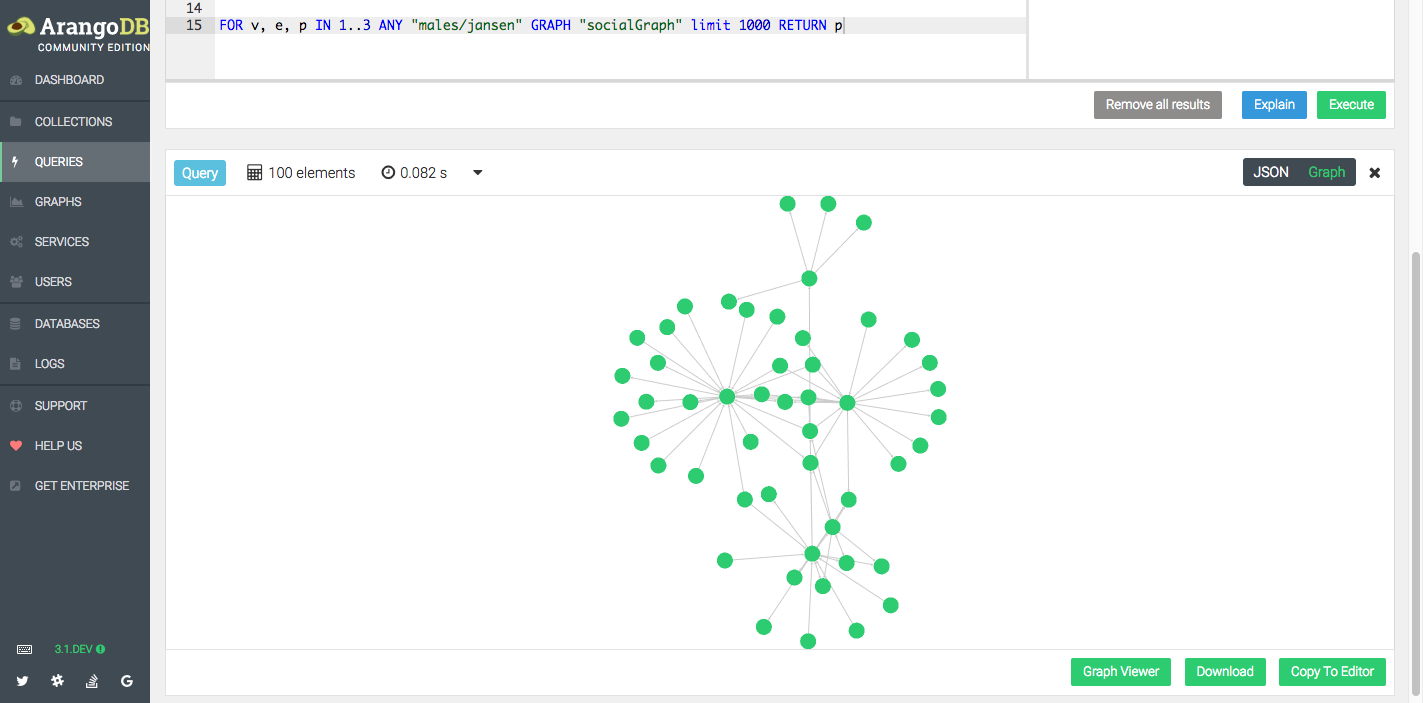
To compute fresh data, delete documents or to manipulate them, queries are used, which select or filter documents as per the given criteria. This architecture is derived from the graph-theoretic concept of a labeled, directed graph, excluding edges that can have not only labels, but can be a complete JSON like document in itself. In practice, a document (read edge) links two documents (read vertices), both stored in their respective collections. Edge collections also store documents, but they are characterized by including two unique attributes, _from and _to for creating relations between documents. There is a subtle difference between these two types. The valve seat has a generally a tubular body having an annular collar having an outer diameter surface extending beyond the outer diameter surface of the tubular body, and an annular insert fabricated of a second material more durable than the first material and affixed to form an inner diameter surface of the collar, the insert forming an. Now we will try to understand ArangoDB's, which requires two kinds of collections - the first is the document collections (known as vertices collections in group-theoretic language), the second is the edge collections. Practically, common characteristics may exist among documents in the collection, however the database system, i.e., ArangoDB itself, does not bind you to a particular data structure. These documents can be saved together in one single collection. However, as a novel feature, ArangoDB is schema-less – there is no a priori reason to specify what attributes the document will have.Īnd unlike RDBMS, each document can be structured in a completely different way from another document. One can compare documents to rows and collections to tables (Here tables and rows refer to those of relational database management systems - RDBMS).īut, in RDBMS, defining columns is a prerequisite to store records into a table, calling these definitions schemas.
Arrays or sub-objects may consist of these data types, which implies that a single document can represent non-trivial data structures.įurther in hierarchy, documents are arranged into collections, which may contain no documents (in theory) or more than one document. A value is either of an atomic type, such as a number, Boolean or null, literal string, or of a compound data type, such as embedded document/object or an array. Zero or more attributes are contained in a document, and a value attached with each attribute. Let us first describe the document based data model.ĪrangoDB's documents closely resemble the JSON format. In this chapter, we will focus on the following topics −ĪrangoDB supports document based data model as well as graph based data model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
